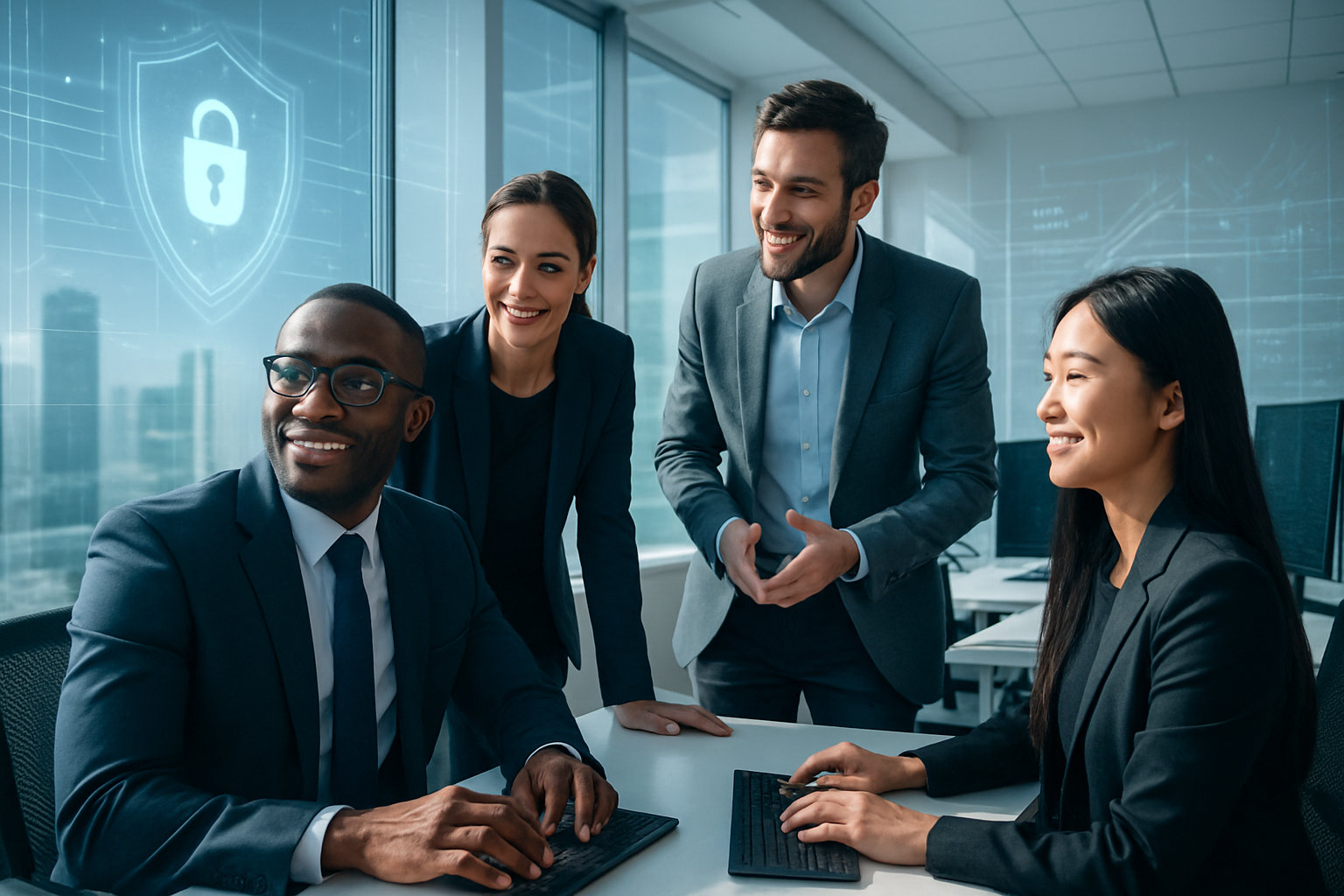
HRMCon 2024 brought together over 1000 registrants with:
- 3 Keynotes
- 4 Tracks & 16 Breakout Sessions
- 22 Speakers
Fill out one form to access all the recordings from this event.







Keynote Speakers
Review extended insights into human risk management from renowned thought leaders in the cybersecurity risk management industry.

The Future Is Now: Introducing Human Risk Management. This is not just a name change. It is a significant change of mindset, strategy, process, and technology about how we approach an old problem in a new world.
Jinan Budge


Jon Brickey
Mastercard | Senior Vice President, Cybersecurity Evangelist
Human Risk Management 2.0
CISOs and their teams need to shift their Security Awareness--aka Human Risk Management (HRM) 1.0--strategies by moving beyond compliance training and phishing simulations and focusing on data, behaviors, insights, and automation. This is the focus of HRM 2.0. Pumping life into Security Awareness is only possible with teamwork across the enterprise and with key vendors.

About Jon
Dr. Jon Brickey is Senior Vice President, Cybersecurity Evangelist, for Mastercard Technology. In this role, he leads the development of cybersecurity strategy, research, innovation, outreach, education & awareness, and technology scouting. Jon supports Corporate Security’s mission of delivering safety and security at the speed of business. He also serves as a Board Member for the Internet Security Alliance.
Before joining Mastercard, Dr. Brickey served in the Army on active duty for over 26 years and retired as a Colonel, holding a variety of leadership and technical roles in information systems management and cyberspace operations. In his last position, he served as the Army Cyber Institute Partner Relations Director for the National Capital Region. Previously, Jon held leadership positions in Cyber-related programs at the National Security Agency, U.S. Cyber Command, Army Cyber Command, U.S. Northern Command, and the U.S. Military Academy at West Point.
Dr. Brickey earned his bachelor’s degree in Political Science from the United States Military Academy at West Point, a master’s degree in Science in Information Technology Management from the Naval Postgraduate School, and a Ph.D. in Computer Science and Information Systems from the University of Colorado Denver. He also holds several industry certifications, including the CISSP, and is a graduate of the Washington University in St. Louis Executive Cybersecurity Leadership Program.

Living Security Blog
Beyond Cybersecurity: Choosing a Human Risk Management Platform
See how human risk management complements traditional cybersecurity, highlighting human behavior, AI-native HRM, and strategies to reduce organizational risk.






